Intelligence-driven solutions to help you stay ahead of account takeover and stay in control

The number of online accounts managed by each individual within an organization results in a vast attack surface for threat actors to target. Account takeover (ATO) attacks see threat actors abuse the trust between the user and the services provided by the account for nefarious purposes, including the authorization of fraudulent transactions, access to protected data, and enabling further cybercrime.
Intel 471 provides unmatched cyber threat intelligence (CTI) to global organizations. You can use this CTI to power security solutions that detect, prevent, and disrupt adversaries committing ATO attacks.
Mass credential theft through the rise of malware like infostealers has lowered the barrier attackers, fueling the underground market and escalating the risk of ATO. We continuously monitor for compromised credentials relevant to your organization and third parties so you can act before they can be exploited. Our sources include infostealer logs, prolific marketplaces, data leak blogs, and dialogue with the threat actors themselves within closed forums and instant messaging channels.
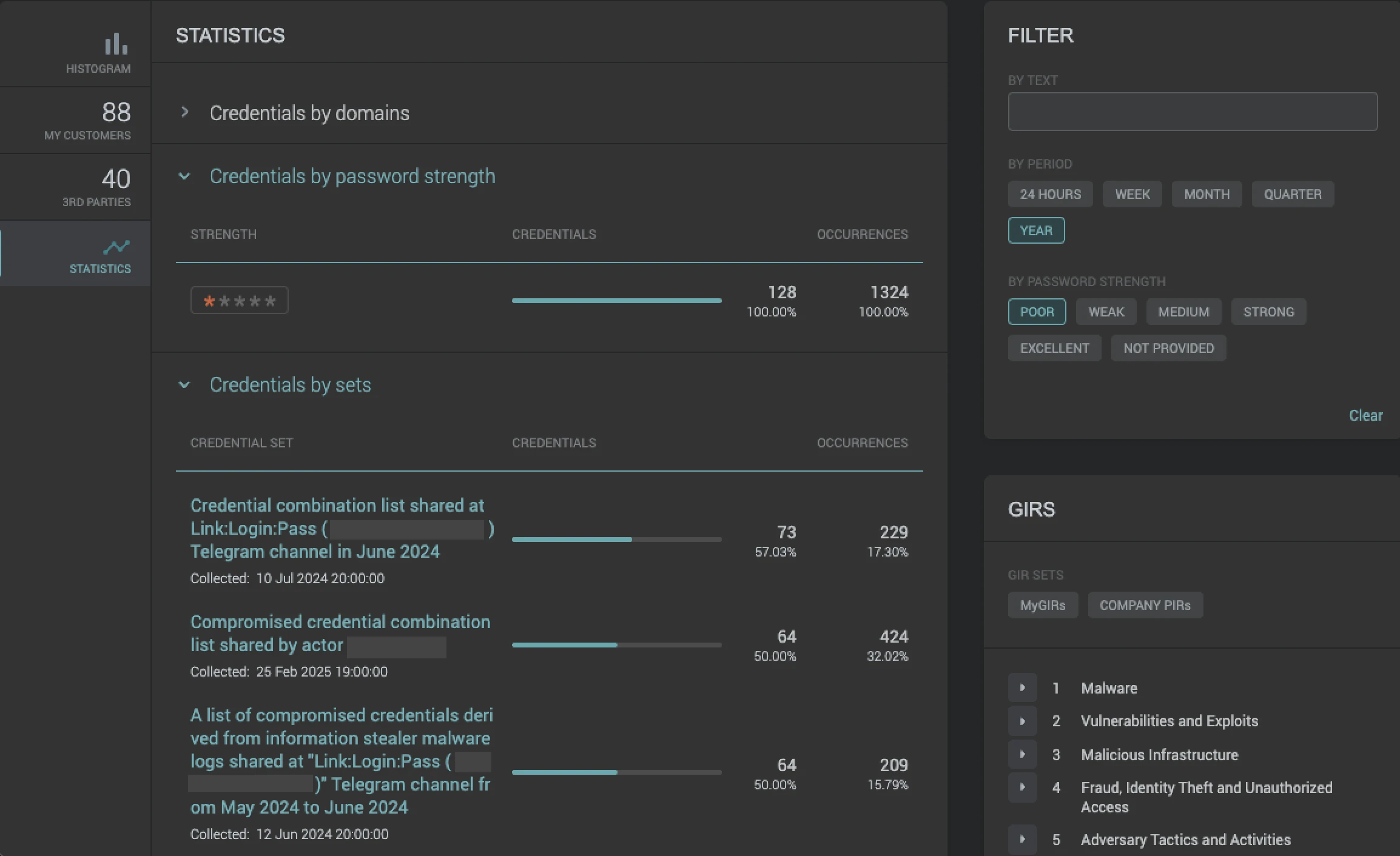
Intuitive filtering of relevant compromised credentials detected from our sources helps users ascertain the source of the credential leak to bolster their security posture for the future.
As well as comprehensive visibility of compromised credentials, you can leverage intelligence reports, malware surveillance data, and dashboards to discern between fresh leaks and repackaged lists of older credentials to prioritize your resources to respond to the threat level appropriately.
Our intelligence teams also track the adversaries and the evolution of threats, giving you the context needed to stay one step ahead of threat actors to proactively protect your organization and its stakeholders. Intel 471’s behavioral threat hunting capabilities also allow you to seek out and disrupt ATO attacks within your organization.
By impersonating a legitimate source or using an emotional appeal, a threat actor can trick an employee into revealing their log in details simply by asking. The threat may already be waiting in your inbox!
Threat actors use tools which automatically generate passwords which the actor then works through in a trial-and-error to attempt to access the user account. Users’ tendency to use simple and recycled passwords renders this method surprisingly effective.
Data breaches are often the result of leaked credentials. When leaked credentials are combined with poor password hygiene, attackers can gain access to multiple accounts. A single entry on a compromised credentials list sold in marketplaces across the underground can mean an account takeover and the potential for multiple cyber attacks, significant loss of sensitive data, and reputational damage.
An increasing number of applications are being connected via your organization’s network. Unknown application vulnerabilities or those that have not yet been patched are an open door for cyber attackers to execute an ATO against your organization.
Intel 471 provides intel-driven solutions to mitigate ATO attacks before they take advantage of your organization.
We continuously monitor activity in key places where threat actors plan, discuss and trade to rapidly alert you to compromised credentials that may trigger ATO.
Map and continuously monitor your external attack surface to identify exposed domains, forgotten authentication portals, and unmonitored endpoints that may be used for credential stuffing to prevent them being used as an attack vector.
We track malware infrastructure, families, campaigns in real-time. Including in-depth intelligence on infostealers, our data ensures you can readily understand attacker infrastructure, the specifics of a malware campaign and high-fidelity technical indicators to not only identify ATOs but harden potential targets against future compromise.
Use Intel 471’s HUNTER threat hunting system to perform intelligence-driven behavioral threat hunts. Perform ‘pre-packaged’ searches for tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs) that evade traditional detection, helping you reduce dwell time and disrupt ATO attacks within your organization’s environment.
Stay informed with our weekly executive update, sending you the latest news and timely data on the threats, risks, and regulations affecting your organization.